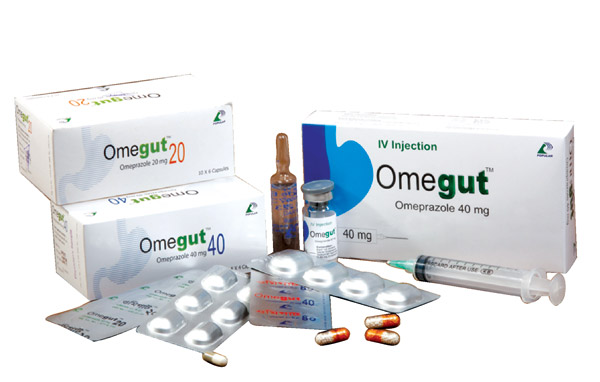
Indication
OmegutTM capsule: OmegutTM capsule is used for the relief of duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), GERD with erosive esophagitis, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, resistant ulcers, eradication of Helicobacter pylori in combination with antibiotics, lesions associated with NSAIDs & prevention of acid aspiration syndrome. OmegutTM IV injection: OmegutTM IV is indicated for the treatment of gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, reflux esophagitis and also for the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Dosage & Administration
Capsule:
|
Disease |
|
Dose |
|
Frequency |
|
Duodenal ulcer |
|
20 mg |
|
Once daily for 4 to 8 weeks |
|
Gastric ulcer |
|
40 mg |
|
Once daily for 4 to 8 weeks |
|
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) |
|
20 mg |
|
Once daily for 4 weeks |
|
GERD with erosive esophagitis |
|
20 mg |
|
Once daily for 4 to 8 weeks |
|
Maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis |
|
20 mg |
|
Once daily * |
|
Zollinger - Ellison syndrome |
|
60 mg |
|
* |
|
Resistant ulcers |
|
* |
|
Once daily for 4 to 8 weeks |
|
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in combination with antibiotics
|
|
20 mg or 40 mg |
|
* |
|
Lesions associated with NSAIDs |
|
20mg to 40 mg |
|
Once daily * |
|
Prevention of acid aspiration syndrome |
|
* |
|
* |
*Depends on the severity of the disease.
Children (over 2 years): Severe ulcerating reflux esophagitis : 0.7-1.4 mg/kg daily for 4-12 weeks; maximum 40 mg daily (to be initiated by hospital pediatricians). Elderly: Dosage adjustment is not required in elderly patients.
OmegutTM IV injection:
In patients with duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer or reflux esophagitis 40 mg once daily is recommended. In patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome the recommended initial dose is 60 mg daily. Higher daily doses may be required and the dose should be adjusted individually. When doses exceed 60 mg daily, the dose should be divided and given twice daily.
Impaired renal function: Dose adjustment is not needed in patients with impaired renal function. Impaired hepatic function: As plasma half-life of Omeprazole is increased in patients with impaired hepatic function, a daily dose of 10 - 20 mg may be sufficient. Elderly: Dose adjustment is not needed in the elderly. Children: 1 month-12 years initially 500 micrograms/kg (max. 20 mg) once daily, increased to 2 mg/kg (max. 40 mg) once daily if necessary. Child 12-18 years: 40 mg once daily.
Method of Administration
Injection: OmegutTM IV injection should be given as a slow intravenous injection. The solution for IV injection is obtained by adding to the vial 10 ml of the solvent provided. After reconstitution the injection should be given slowly over a period of at least 2.5 minutes at a maximum rate of 4 ml per minute. The solution should be used within 4 h of reconstitution when stored in original vial in a cool place. The reconstituted solution should not be used if it contains visible particulate matter. Infusion: For IV infusion reconstitute one sterile single dose vial of OmegutTM IV injection with the provided 10 ml solvent in ampoule to make 10 ml solution containing 4 mg/ml of Omeprazole approximately. Subsequently add 10 ml of reconstituted solution containing 4 mg/ml of Omeprazole approximately, to 90 ml 0.9% Sodium Chloride solution or 90 ml of 5% Dextrose solution to make 100 ml solution of 0.4 mg/ml of Omeprazole approximately. The resultant infusion should be given intravenously over a period of 20-30 minutes. Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 12 h after reconstitution with saline or for 6 h after reconstitution with 5% Dextrose. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. Any unused portion should be discarded.
Precautions
Omeprazole should be given in reduced dosage to patients with impaired hepatic function. Use in pregnancy: Results from three prospective epidemiological studies indicate no adverse effects of Omeprazole on pregnancy or on the health of the fetus/newborn child. Omeprazole can be used during pregnancy. Use in lactation: Omeprazole is excreted in breast milk but is not likely to influence the child when therapeutic doses are used. Like other drugs it should only be used during nursing if considered essential.